
This method has largely been replaced by the kinematic viscosity method.

The efflux time is Saybolt Universal Seconds ( SUS) required for 60 milliliters of a petroleum product to flow through the calibrated orifice of a Saybolt Universal viscometer - under a carefully controlled temperature and as prescribed by test method ASTM D 88. Saybolt Universal Seconds (or SUS) is an alternative unit for measuring viscosity.

Other Viscosity Units Saybolt Universal Seconds (or SUS, SSU)
VISCOSITY FORMULA FLUID MECHANICS OFFLINE
This is a free app that can be used offline on mobile devices. Related Mobile Apps from The Engineering ToolBox for a gas - the kinematic viscosity increases with higher temperature.for a liquid - the kinematic viscosity decreases with higher temperature.For a distillate fluid the reference temperature is 40 oC.
VISCOSITY FORMULA FLUID MECHANICS ISO
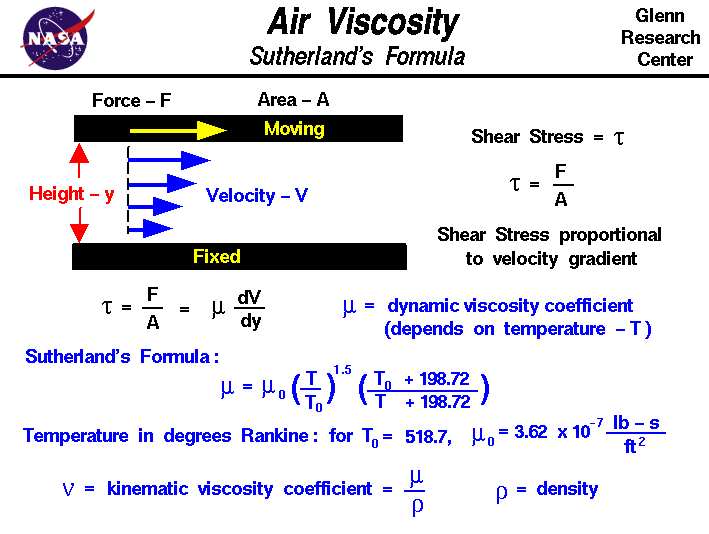
In ISO 8217 the reference temperature for a residual fluid is 100 oC. The viscosity of a fluid is highly temperature dependent - and for dynamic or kinematic viscosity to be meaningful the reference temperature must be quoted. Kinematic viscosity of common liquids and fluidsĪ conversion from absolute to kinematic viscosity in Imperial units can be expressed as.A more exact kinematic viscosity for water at 20.2 oC (68.4 oF) is 1.0038 mm 2/s (cSt).
The specific gravity for water at 20.2 oC (68.4 oF) is almost one, and the kinematic viscosity for water at 20.2 oC (68.4 oF) is for practical purpose 1.0 mm 2/s (cStokes). Since the Stoke is a large unit it is often divided by 100 into the smaller unit centiStoke (cSt) - where Stoke comes from the CGS (Centimetre Gram Second) unit system. In the SI-system the theoretical unit of kinematic viscosity is m 2/s - or the commonly used Stoke (St)where Μ = absolute or dynamic viscosity (N s/m 2) Kinematic viscosity can be obtained by dividing the absolute viscosity of a fluid with the fluid mass density like Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of - absolute (or dynamic) viscosity to density - a quantity in which no force is involved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
